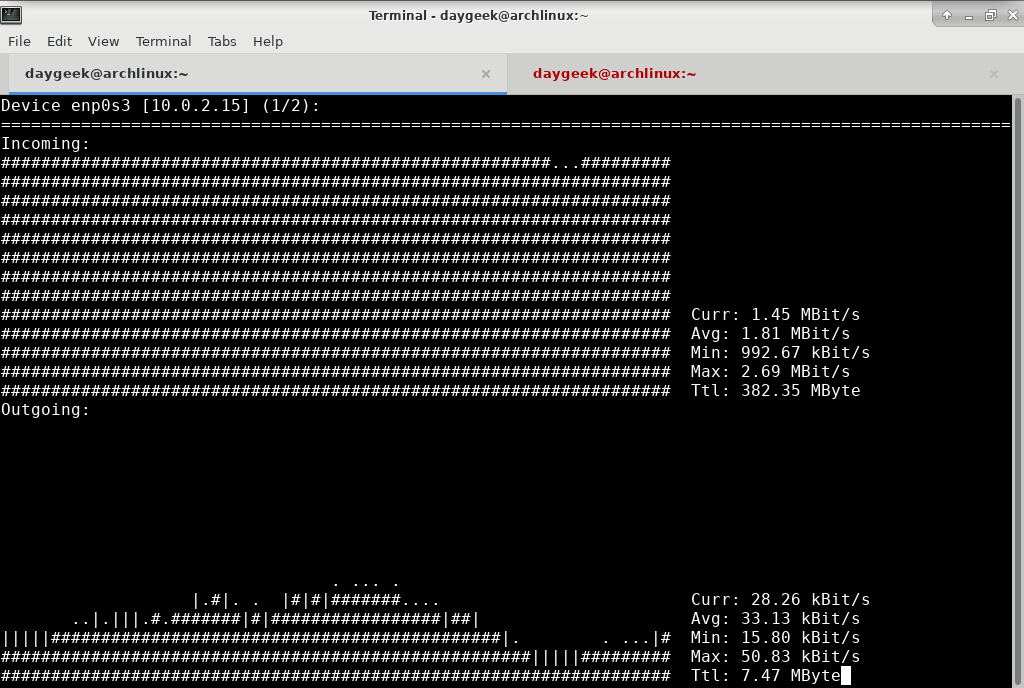
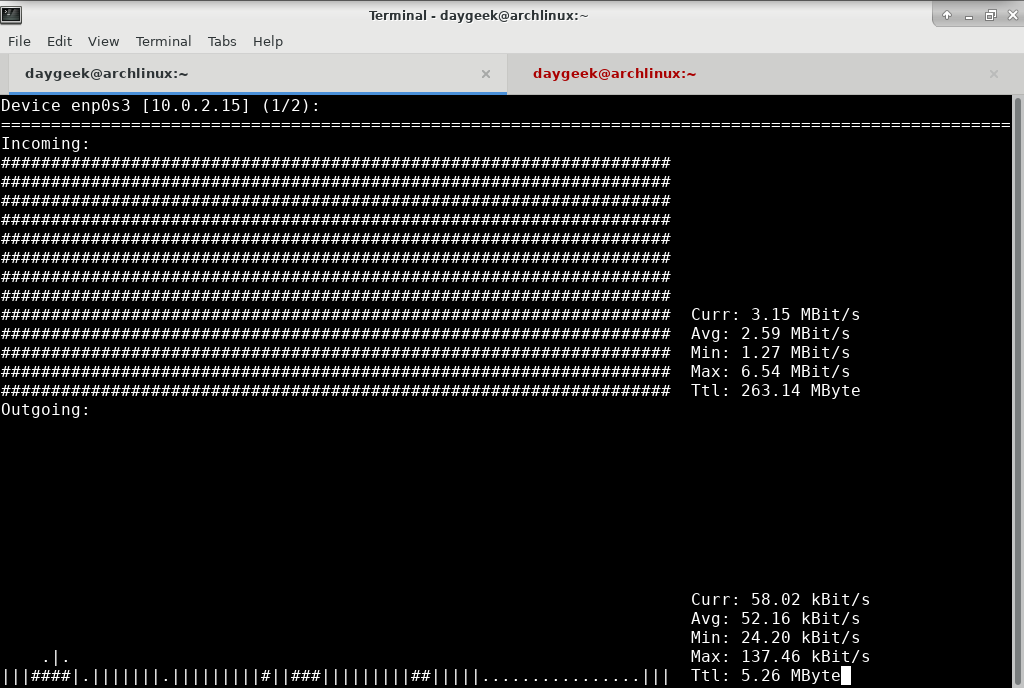
Nload is a console application which monitors network traffic and bandwidth usage in real time.
It displays the total amount of data that has been transfered over a network device since the last reboot, the current bandwidth usage, and the minimum, maximum, and average bandwidth usage measured since it started.
It visualizes the in coming and outgoing traffic using two graphs and provides additional info like total amount of transfered data and min/max network usage.
You can switch between the devices by pressing the left and right arrow keys. To display altogether in one screen, add -m parameter with nload. If you want to quit, simply hit q or Ctrl+c.
Suggested Read :
(#) vnStat – A lightweight (Command Line) Network Traffic Monitoring Tool
(#) bmon – Real Time Bandwidth Monitor and Rate Estimator in Linux
The default value of interval is 500 milliseconds which we can modify by passing -t parameter followed by interval number in millisec. Make a note, specifying refresh intervals shorter than about 100 milliseconds makes traffic calculation very unprecise.
Also we can monitor particular device (interface) by passing interface name with nload command.
How to install Nload on Linux
nload is available in distribution official repository, so use your package manager to install it.
For Arch Linux based systems, nload package is available in distribution official repository, so use Pacman command to install it.
$ sudo pacman -S nload
For Debian/Ubuntu based systems, nload package is available in distribution official repository, so use APT or APT-GET command to install it.
$ sudo apt-get install nload
For openSUSE systems, nload package is available in distribution official repository, so use Zypper command to install it.
$ sudo zypper install nload
For RHEL/CentOS systems, nload package is not available in distribution official repository, so enable EPEL repository then use YUM command to install it.
$ sudo yum install nload
For Fedora systems, nload package is available in distribution official repository, so use DNF command to install it.
$ sudo dnf install nload
How to use Nload
Run the nload command without any option to get default output. Hit left and right arrow keys to switch between the devices.
$ nload
To monitor particular device (interface), run the following command.
$ nload enp0s3
Press F2 to show the option window, Press F5 to save current settings, and Press F6 reload settings from the config files.
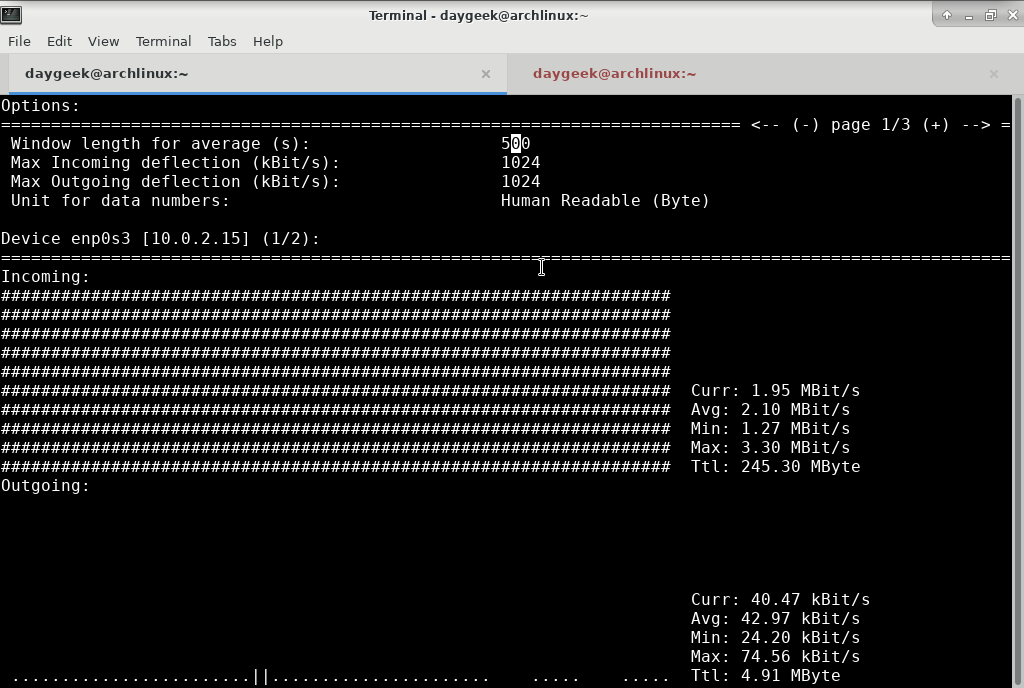
To monitor network usage with different interval, run the following command.
$ nload -t 700
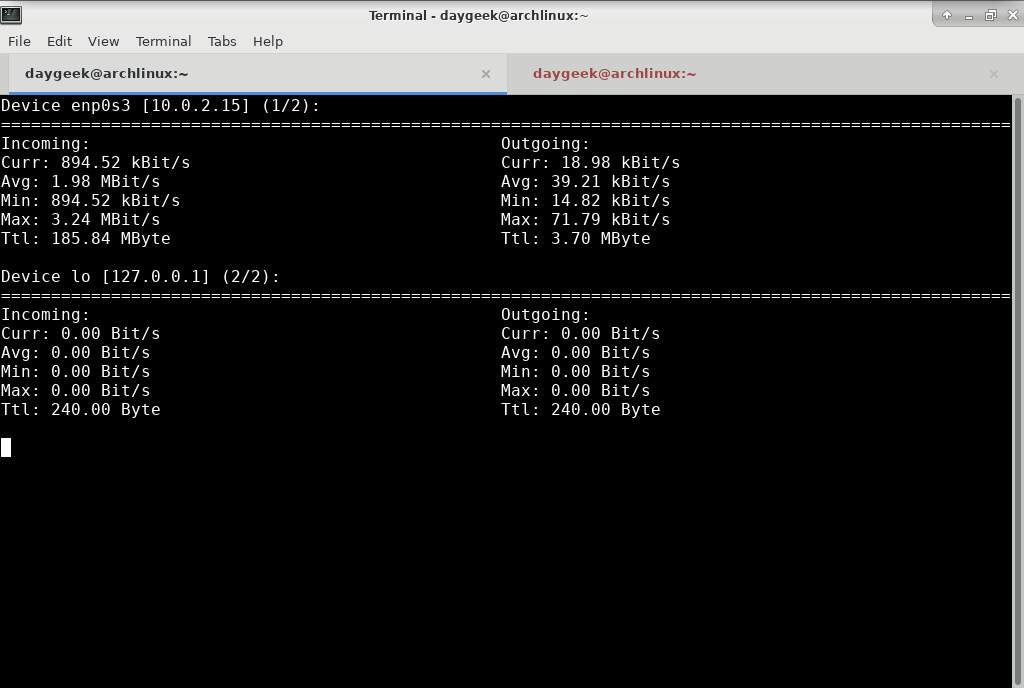
To monitor altogether (All devices) in one screen, run the following command.
$ nload -m
Navigate to man page for more details about nload.
$ man nload or $ nload --help nload version 0.7.4 Copyright (C) 2001 - 2012 by Roland Riegel <[email protected]> nload comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions. For more details see the GNU General Public License Version 2 (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.html). Command line syntax: nload [options] [devices] nload --help|-h Options: -a period Sets the length in seconds of the time window for average calculation. Default is 300. -i max_scaling Specifies the 100% mark in kBit/s of the graph indicating the incoming bandwidth usage. Ignored if max_scaling is 0 or the switch -m is given. Default is 10240. -m Show multiple devices at a time; no traffic graphs. -o max_scaling Same as -i but for the graph indicating the outgoing bandwidth usage. Default is 10240. -t interval Determines the refresh interval of the display in milliseconds. Default is 500. -u h|b|k|m|g Sets the type of unit used for the display of traffic numbers. H|B|K|M|G h: auto, b: Bit/s, k: kBit/s, m: MBit/s etc. H: auto, B: Byte/s, K: kByte/s, M: MByte/s etc. Default is h. -U h|b|k|m|g Same as -u, but for a total amount of data (without "/s"). H|B|K|M|G Default is H. devices Network devices to use. Default is to use all auto-detected devices. --help -h Print this help. example: nload -t 200 -i 1024 -o 128 -U M The options above can also be changed at run time by pressing the 'F2' key.