MongoDB team proudly announced the release of new version of mongoDB 3.2.3 on February 13, 2016. MongoDB 3.2 introduces new storage engines that extend the capabilities of the database & MongoDB 3.2.3 released with minor bug fixes. mongoDB is an opensource, simple, Flexible Data Model, Highly Scalable and NoSQL database. It stores data as a document for high performance compared with SQL databases.
MongoDB Packages
- mongodb-org : This is the main package for MongoDB which will install all required below supporting packages.
- mongodb-org-server : This package contains the mongos daemon and associated configuration and init scripts.
- mongodb-org-mongos : This package contains the mongos daemon.
- mongodb-org-shell : This package contains the mongo shell.
- mongodb-org-tools : This package contains lot of MongoDB tools which will perform all the operations like backup, restore and repair, etc..,
MongoDB tools and usage
- mongoimport : The mongoimport tool, import content from a JSON, CSV, or TSV export created by mongoexport, or another third-party export tool.
- bsondump : The bsondump converts BSON files into human-readable formats including JSON. For example, bsondump is useful for reading the output files generated by mongodump.
- mongodump : mongodump is an utility for creating a binary export of the contents of a database.
- mongoexport : mongoexport is an utility that produces a JSON or CSV export of data stored in a MongoDB instance.
- mongofiles : The mongofiles utility makes it possible to manipulate files stored in your MongoDB instance in GridFS objects from the command line.
- mongooplog : mongooplog is a simple tool that polls operations from the replication oplog of a remote server, and applies them to the local server.
- mongoperf : mongoperf is an utility to check disk I/O performance independent of MongoDB.
- mongorestore : The mongorestore program writes data from a binary database dump created by mongodump to a MongoDB instance. mongorestore can create a new database or add data to an existing database.
- mongostat : The mongostat utility provides a quick overview of the status of a currently running mongod or mongos instances.
- mongotop : mongotop provides a method to track the amount of time a MongoDB instance spends on reading and writing data.
1) Add MongoDB repository to CentOS/RHEL 6.2+ & 7.0+
Create a /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-3.2.repo file and add MongoDB repository on your system.
$ sudo /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-3.2.repo [mongodb-org-3.2] name=MongoDB Repository baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/3.2/x86_64/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
1a) Add MongoDB repository to Ubuntu 12.04 & 14.04
Use the below commands to add MongoDB repository on your system.
# Import MongoDB Public GPGkey # $ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv EA312927 # Create MongoDB repository # $ echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu "$(lsb_release -sc)"/mongodb-org/3.2 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.2.list # Update your system repository list # $ sudo apt-get update
1b) Add MongoDB repository to Debian 7
Use the below commands to add MongoDB repository on your system.
# Import MongoDB Public GPGkey # $ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv EA312927 # Add MongoDB repository to Debian # $ echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian "$(lsb_release -sc)"/mongodb-org/3.2 main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.2.list # Update your system repository list # $ sudo apt-get update
2) Install the MongoDB packages
Use the below commands to install MongoDB packages on your system.
# Installing MongoDB packages to Ubuntu/Mint/Debian systems # $ sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org # Installing MongoDB packages to RHEL/CentOS systems # $ sudo yum install -y mongodb-org # Installing a specific release of MongoDB to deb based system # sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org=3.2.1 mongodb-org-server=3.2.1 mongodb-org-shell=3.2.1 mongodb-org-mongos=3.2.1 mongodb-org-tools=3.2.1 # Installing a specific release of MongoDB to RHEL based system # sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org=3.2.1 mongodb-org-server=3.2.1 mongodb-org-shell=3.2.1 mongodb-org-mongos=3.2.1 mongodb-org-tools=3.2.1
3) Configuring MongoDB Database
Open /etc/mongod.conf and uncomment the below lines, if it is commented else leave it.
# Configuring MongoDB config file #
sudo nano /etc/mongod.conf
dbpath=/var/lib/mongo
logpath=/var/log/mongo/mongod.log
port=27017
4) Start MongoDB Database
Use the below command to KICK START your newly installed MongoDB.
# Start MongoDB Service # $ sudo service mongod start # Start MongoDB as a Daemon # $ mongod
5) Install MongoDB from source
Use the below steps to install MongoDB from source.
# cd /opt # curl -O https://fastdl.mongodb.org/linux/mongodb-linux-x86_64-3.2.1.tgz # tar -zxvf mongodb-linux-x86_64-3.2.1.tgz # mkdir -p mongodb # mkdir -p /data/db # cd mongodb-linux-x86_64-3.2.1 # mv * /opt/mongodb # cd /opt/mongodb/bin # ./mongod
Open separate terminal and open the mongodb shell.
# cd /opt/mongodb/bin # ./mongo
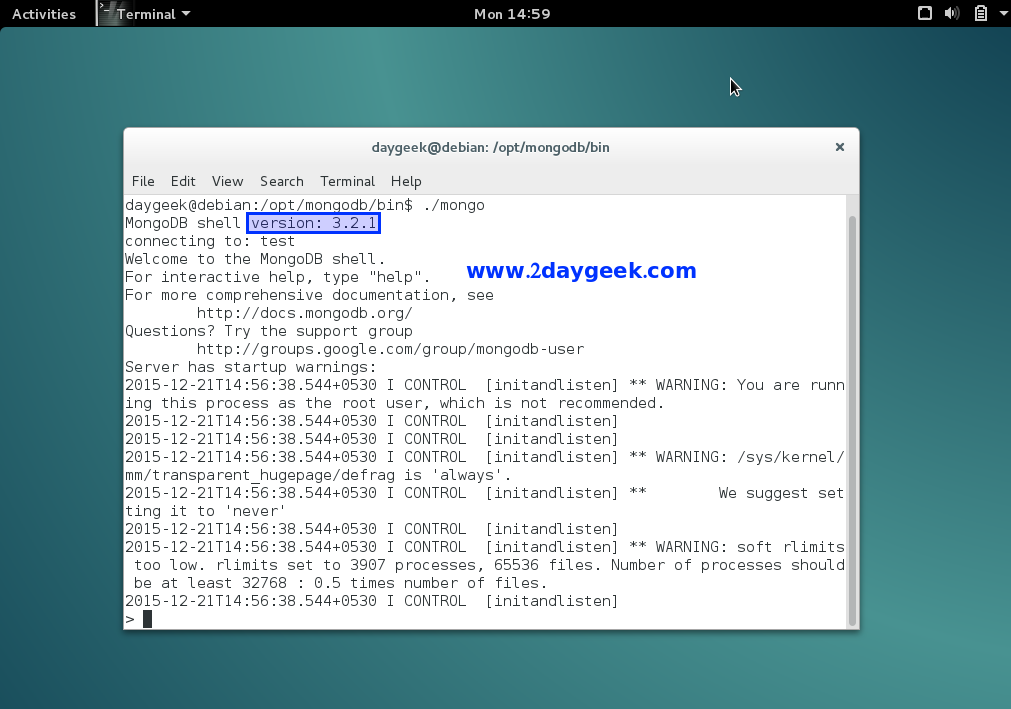
6) MongoDB Daemon issue
When i’m trying to start MongoDB, i got below error message. By default MongoDB stores data’s to /data/db folder but by default it wont be created. So, we need to mention the path name which is in /etc/mongod.conf file use the below command then try again.
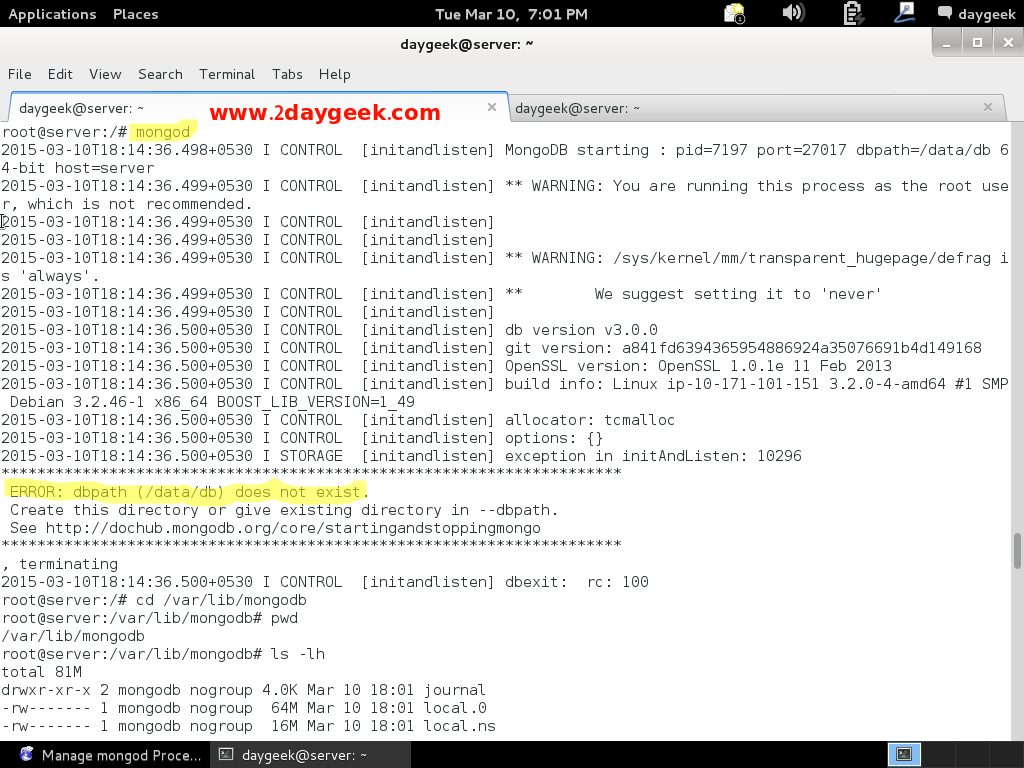
# MongoDB Daemon issue : Solution # $ sudo mongod --dbpath /var/lib/mongodb # Greping existing session PID # $ netstat -tulpn | grep :27017 # Killing existing session # $ sudo kill -9 PID of above output # Start MongoDB as a Daemon # $ sudo mongod
7) Accessing MongoDB shell
Accessing MongoDB shell to perform whatever you want.
# Accessing MongoDB shell #
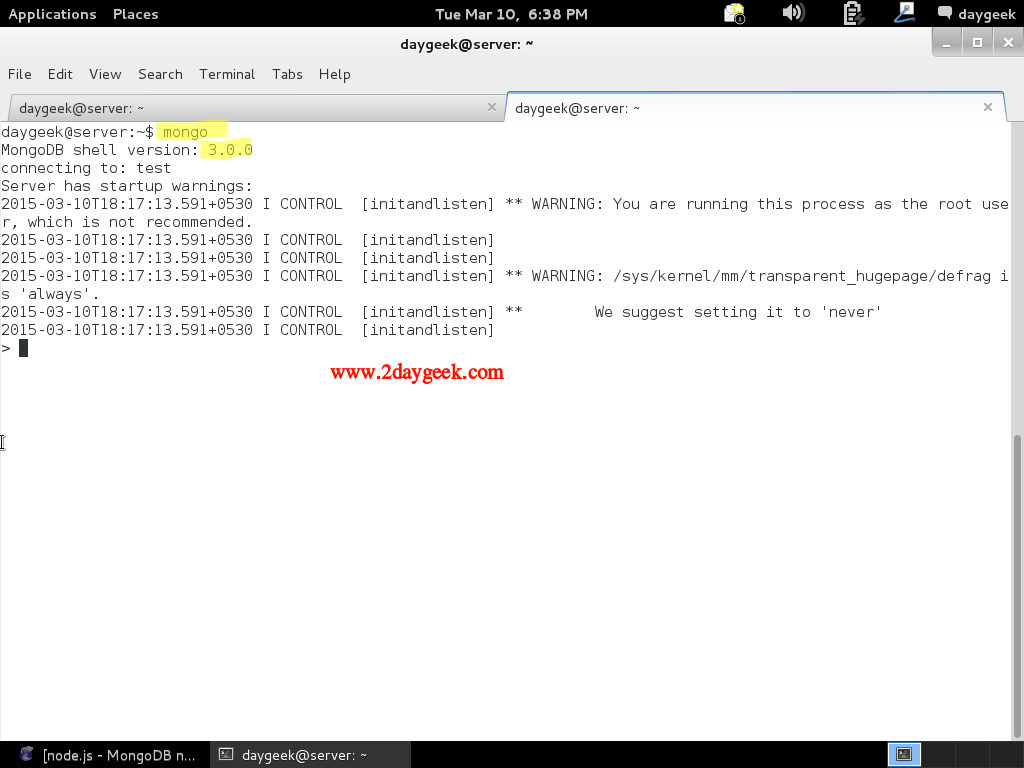
$ sudo mongo
See the below output for MongoDB shell.
Some big IT companies using




Hello Magesh, Just updated to mongodb, thanks a lot for this wonderful guide. it helped me a lot. Cheers!
@Tish,
Welcome.