Stacer is an open source system optimizer and Application Monitor that helps users to manage entire system with different aspects. The app will prompt you to enter the sudo password most of the time to perform the action since it uses gksudo. If you failed to enter sudo password or wrong password will leads to fail many action in background but in front-end the app still run as a normal user.
In straight forward, it’s doing many activity instead of specific one, so we can say in another hand, its all in one system utility.
Stacer Features:
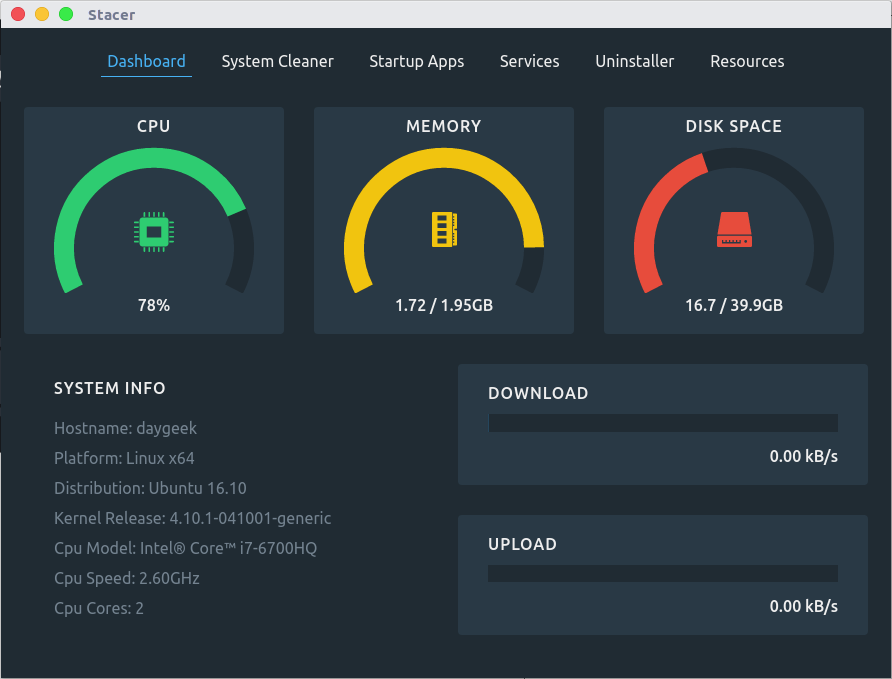
- Dashboard : Display the system information & current system resource usage.
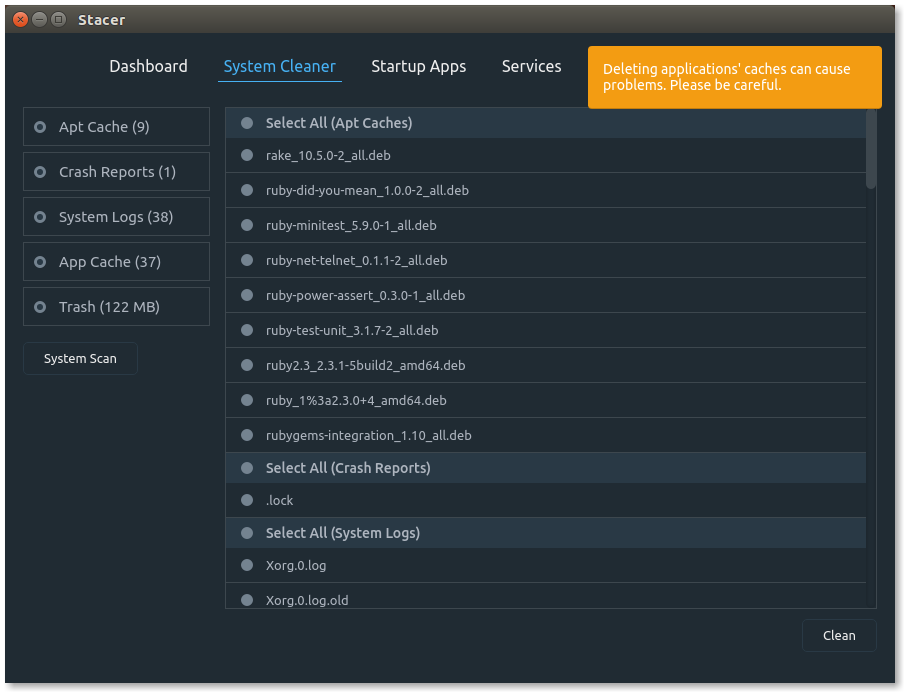
- System Cleaner : Helps users to clean the variety of system caches, Its work similar to Ubuntu system cleaner and bleachbit.
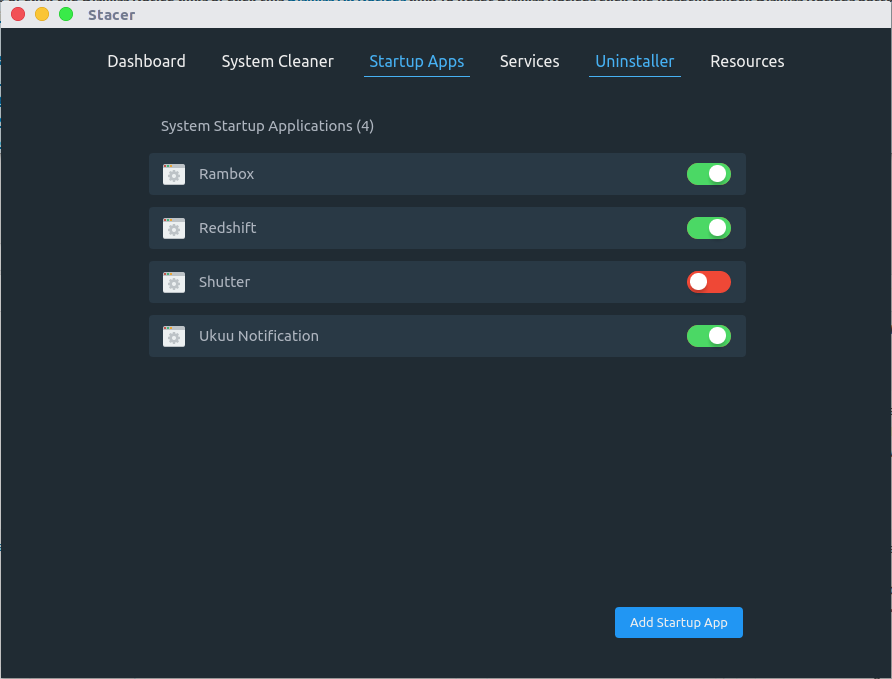
- Startup Apps : We can easily add, enable & disable startup applications.
- Services : Easily enable & disable system services.
- Uninstaller : Remove the unused applications through stacer.
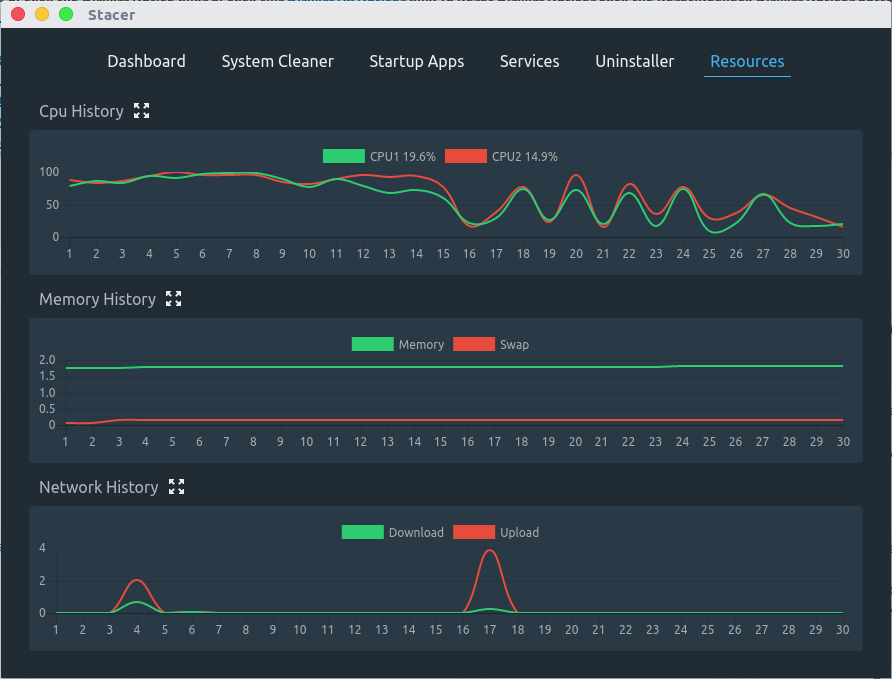
- Resources : We can see the detailed graph about CPU, Memory & Network utilization.
How to install Stacer in Debian ?
Navigate to developer GitHub page and download the latest available version of dep file, then use DPKG Package Manager to install the package.
$ wget https://github.com/oguzhaninan/Stacer/releases/download/v1.0.6/Stacer_1.0.6_amd64.deb $ sudo dpkg -i Stacer_1.0.6_amd64.deb
How to install Stacer in Linux ?
All other Linux distribution users can easily install the Stacer package by downloading the latest AppImage file from developer GitHub page download.
$ wget https://github.com/oguzhaninan/Stacer/releases/download/v1.0.6/Stacer-1.0.6-x86_64.AppImage $ sudo chmod +x Stacer-1.0.6-x86_64.AppImage $ ./Stacer-1.0.6-x86_64.AppImage
Dashboard
In Dashboard, users can see the system information (including Host name, Arch, Distribution name, Kernel information, CPU Model, CPU Speed & CPU Cores) & current system resource usage (including CPU Utilization, Memory Utilization, Disk space utilization & real time network stats – Upload/Download info)
System Cleaner
It helps users to clean the variety of system caches (including package manager cache, system logs, Application cache, etc,.), this will warns when you trying to clean the caches. App caches occupy lot of disk space but save more bandwidth so, make sure before clearing the app caches. Its works similar to Ubuntu system cleaner and bleachbit.
Startup Apps
Here you can see list of apps which are going to startup ASAP after system boot, it may slow down the system startup or consume more resources in certain time after system boot. Verify the startup applications and remove unwanted apps that you don’t want to startup after login.
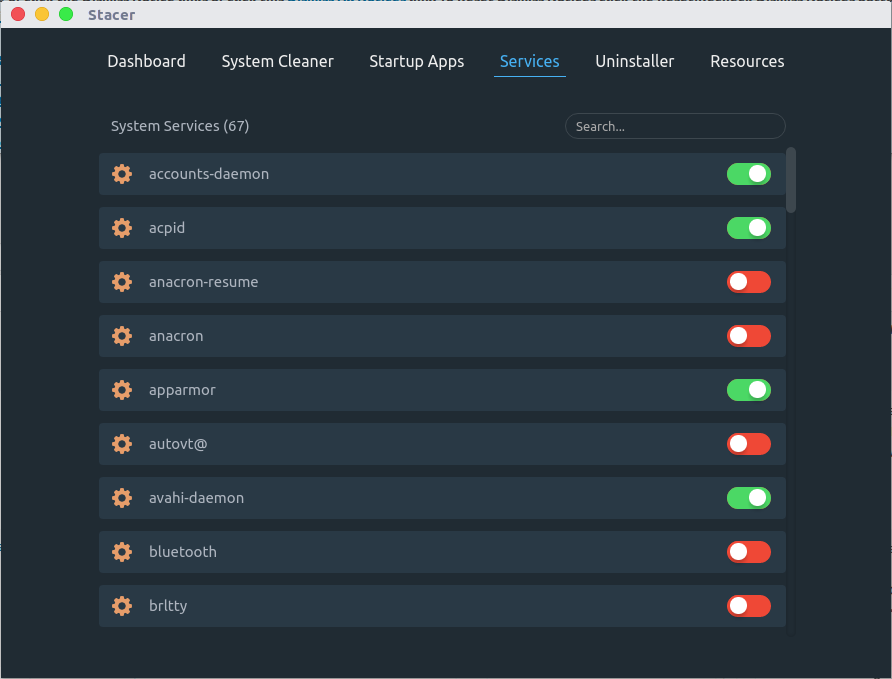
Services
Enable and Disable unused system services by simple clicking the button ON/OFF.
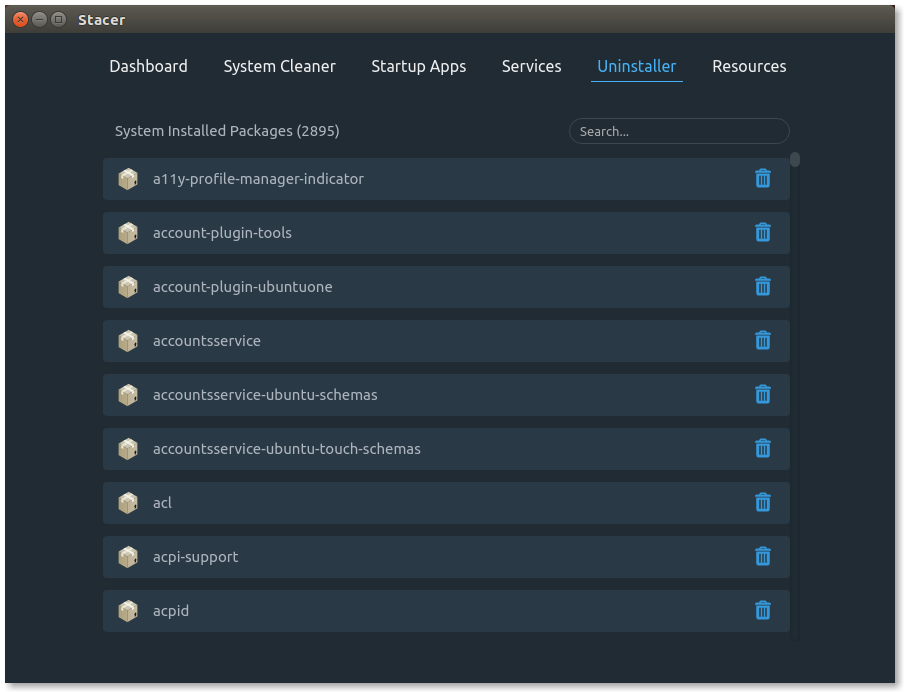
Uninstaller
It’s similar to GUI package manager that helps newbies to safely remove the packages from system (Make a note, you can see all the installed packages including core, so be careful while performing the package removal)
Resources
This section added newly to monitor system resources in depth. We can see the detailed graph about CPU utilization (Each CPU activity), Memory utilization (Memory and swap) & Network utilization (real time upload/download network stats).