zypper is a command line tool for package management in openSUSE and SUSE Enterprise Linux. It using the 'libzypp' library for installing, updating, searching and removing packages a well as for managing repositories, perform various queries, and more.
Common syntax:
The general syntax of zypper is as follow:
zypper [--global-options] command [--command-options] [arguments]
File location:
Important ‘zypper’ configuration files are as follows:
| File | Usage |
|---|---|
| /etc/zypp/zypper.conf | Main zypper configuration file |
| /var/cache/zypp | zypper cached file location |
| /var/log/zypp/history | zypper history file |
| /usr/lib/zypper/commands | zypper subcommands executables location |
1) Refreshing repositories
When you add a new repository or the repository expires you will need to run the below zypper command to update the repository. It downloads package metadata from repositories.
$ sudo zypper ref or $ sudo zypper refresh Repository 'Atom Editor' is up to date. Repository 'Google-Chrome' is up to date. Repository 'google-chrome' is up to date. Repository 'packman' is up to date. Repository 'Non-OSS Repository' is up to date. Repository 'Main Repository' is up to date. Repository 'Main Update Repository' is up to date. Repository 'Update Repository (Non-Oss)' is up to date. All repositories have been refreshed.
2) Installing packages
To install packages, use the following zypper command:
sudo zypper install PACKAGE_NAME
If you already know the exact package name, run: For instance, to install ‘apache2’ package run:
$ sudo zypper install apache2 or $ sudo zypper in apache2
To install a package with a specific version number, run:
$ sudo zypper in apache2-2.4.43
To install a pattern package, run: This install LAMP Stack on your system with single command.
$ sudo zypper in -t pattern lamp_server
To install a rpm package that is available in the local path, run:
$ sudo zypper /path/to/file.rpm
To install a rpm package from remote path, run:
$ sudo zypper https://xyz.com/file.rpm
To install and remove packages simultaneously, use the '+/-' modifiers. To install ‘vim’ and simultaneously remove ‘nano’, run:
$ sudo zypper install vim -nano
To remove ‘vim’ and simultaneously install ’emacs’, run:
$ sudo zypper install vim +emacs
3) Removing packages
The zypper removal command is similar to the installation command, except that the effect is opposite.
sudo zypper remove PACKAGE_NAME
To remove a package, run: For instance, to remove ‘apache2’ package, run:
$ sudo zypper remove apache2 or $ sudo zypper re apache2
If you automatically want to remove any dependencies that become unused after removing the specified package, run:
$ sudo zypper rm --clean-deps PACKAGE_NAME
4) Updating Patches
There are two different ways to update packages using zypper on openSUSE and SUSE Enterprise Linux.
- Installing patches
- Installing all the available updates
To install all officially released patches, run:
$ sudo zypper patch
The above command does not apply patches from third party repositories. To install all together, run:
$ sudo zypper patch --with-update
To install patches related to a specific Bugzilla issue, run
$ sudo zypper patch --bugzilla=NUMBER
To install a security patch related to a specific CVE number, run:
$ sudo zypper patch --cve=NUMBER
5) Listing patches
You can check available patches on your system using the following two commands.
To list the number of patches to be installed, run:
$ sudo zypper patch-check Loading repository data… Reading installed packages… 0 patches needed (0 security patches)
To list actual patches with details, run:
$ sudo zypper list-patches Loading repository data… Reading installed packages… No updates found.
6) Managing Repositories with zypper
The zypper command has numerous options for managing repositories.
- Listing all repositories
- Adding repositories
- Removing repositories
- Modifying repositories
6.1) Listing all Repositories
To list all repositories active on the system, run:
$ zypper repos
Repository priorities in effect:
(See 'zypper lr -P' for details)
90 (raised priority) : 1 repository
99 (default priority) : 7 repositories
# | Alias | Name | Enabled | GPG Check | Refresh
---+---------------------------+------------------------------------+---------+-----------+--------
1 | Atom | Atom Editor | Yes | (r ) Yes | No
2 | Google-Chrome | Google-Chrome | Yes | (r ) Yes | No
3 | google-chrome | google-chrome | Yes | (r ) Yes | Yes
4 | openSUSE-Leap-15.2-1 | openSUSE-Leap-15.2-1 | No | ---- | ----
5 | packman | packman | Yes | (r ) Yes | Yes
6 | repo-debug | Debug Repository | No | ---- | ----
7 | repo-debug-non-oss | Debug Repository (Non-OSS) | No | ---- | ----
8 | repo-debug-update | Update Repository (Debug) | No | ---- | ----
9 | repo-debug-update-non-oss | Update Repository (Debug, Non-OSS) | No | ---- | ----
10 | repo-non-oss | Non-OSS Repository | Yes | (r ) Yes | Yes
11 | repo-oss | Main Repository | Yes | (r ) Yes | Yes
12 | repo-source | Source Repository | No | ---- | ----
13 | repo-source-non-oss | Source Repository (Non-OSS) | No | ---- | ----
14 | repo-update | Main Update Repository | Yes | (r ) Yes | Yes
15 | repo-update-non-oss | Update Repository (Non-Oss) | Yes | (r ) Yes | Yes
6.2) Listing Repositories with URI
$ zypper lr -u
6.3) Listing Repositories with priority
$ zypper lr -p
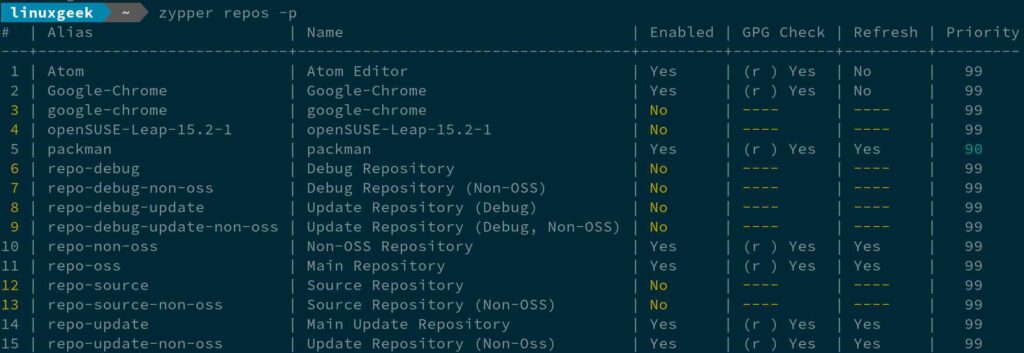
6.4) Refreshing a specific Repositories
$ sudo zypper ref Atom Repository 'Atom Editor' is up to date. Specified repositories have been refreshed.
6.5) Disabling a specific Repositories
$ sudo zypper mr -d google-chrome Repository 'google-chrome' has been successfully disabled.
6.6) Enabling a specific Repositories
$ sudo zypper mr -e 1 Repository 'google-chrome' has been successfully enabled.
6.7) Ading a new Repository
$ sudo zypper addrepo -cfp 90 'https://ftp.gwdg.de/pub/linux/misc/packman/suse/openSUSE_Leap_$releasever/' packman
6.8) Removing a Repository
$ sudo zypper rr packman-repository or $ sudo zypper removerepo repo-no Removing repository 'packman-repository' .......................[done] Repository 'packman-repository' has been removed.
7) Querying Packages with zypper
zypper offers various methods to query packages.
To get lists of all products, run:
$ zypper products
To get lists of all patterns, run:
$ zypper patterns
To get lists of all packages, run:
$ zypper packages
8) Searching Packages
If you do not know the exact package name that you want to install. Use the search option with zypper command, which will return the matching string based on the given input text. For example, to see a list of ftp packages, run:
$ zypper search ftp or $ zypper se ftp
9) Checking package information
To find out detailed information about a package, run. It will give you package version, size, repo name, package version, architecture etc.
$ zypper info apache2
10) Checking Updates
A list of availble package updates can be obtained with the following command.
$ zypper list-updates
11) Updating Packages
To update all installed packages with newer available versions, run:
$ sudo zypper update or $ sudo zypper up
12) Installing Missing Dependencies
To verify whether all dependencies are still fulfilled or not by running the below command.
$ sudo zypper verify
If you found missing dependencies, run the below command to repair it.
$ sudo zypper install-new-recommends
13) Rebuilding database
If you have trouble accessing the packages in the configured repositories after the ‘zypper refresh’, execute the below command: This forces a complete refresh and rebuild of the database, including a forced download of raw metadata.
$ sudo zypper refresh -fdb
14) Cleaning zypper Cache
zypper command cache can be cleared using the below commands:
To clean zypper cache only, run:
$ sudo zypper clean
To clean metadata and package cache at once, run:
$ sudo zypper clean -a or $ sudo zypper clean --all
15) zypper command help
To get a help from zypper command and know more about it, run:
To list the available global options and commands, run:
$ zypper
Print help for a specific command
$ zypper help [command]
For more information, run:
$ man zypper
and
$ zypper --help
Conclusion
This tutorial explains how to manage packages using ‘zypper’ command in openSUSE and SUSE Enterpise Linux systems.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to comment below and we shall get back to you as soon as possible. Happy learning!



